Bibliometric-patentometric analysis of scientific-technological alternatives for the treatment of industrial water and waste using natural and/or modified zeolites
Main Article Content
Abstract
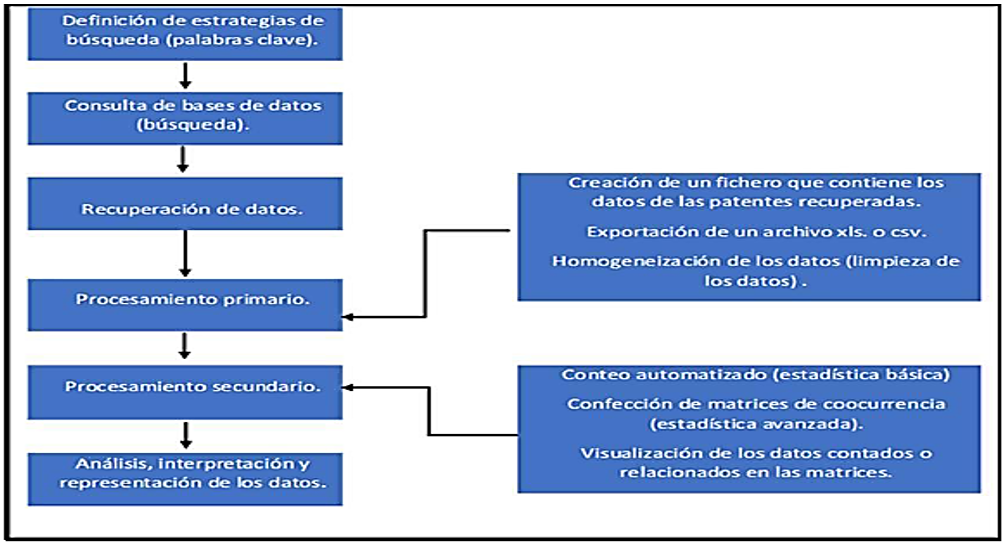
The objetive of this work is to analyze the scientific –technological production for the treatment of water and industrial waste using natural and /or modified zeolites,through bibliometric and patentometric studies. The research required the use of different theoretical Methods such as the analytical –synthetic, the inductive –deductive, and the empirical method for classic documentary analysis. The results showed that scientific advances in the use of modified natural zeolite for the removal of heavy metals and ammonium are relevant. It is concluded that scientific and technological production on this topic has made important advances in the period studied in question (2010-2020).
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Those authors who have publications with this journal accept the following terms:
- The authors will retain their copyright and guarantee the magazine the right to first publish their work, which will be simultaneously subject to the Creative Commons 4.0 Recognition-NonCommercial Recognition License that allows third parties to share the work whenever it is indicate its author and its first publication this magazine. Under this license the author will be free from:
- Share - copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format
- Adapt - remix, transform and create from the material
- The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms while complying with the terms of the license
Under the following conditions:
- Recognition - You must properly recognize the authorship, provide a link to the license and indicate if changes have been made. You can do it in any reasonable way, but not in a way that suggests that you have the support of the licensor or receive it for the use you make.
- NonCommercial - You may not use the material for a commercial purpose.
- There are no additional restrictions - You cannot apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict what the license allows.
- Authors may adopt other non-exclusive licensing agreements for the distribution of the version of the published work (e.g., deposit it in an institutional telematic archive or publish it in a monographic volume) provided that the initial publication in this journal is indicated.
- Authors are allowed and recommended to disseminate their work through the Internet (e.g., in institutional telematic archives or on their website) before and during the submission process, which can produce interesting exchanges and increase citations. of the published work. (See The effect of open access).
The magazine is not responsible for the opinions and concepts issued in the works, they are the sole responsibility of the authors. The Editor, with the assistance of the Editorial Committee, reserves the right to suggest or request advisable or necessary modifications. The mention of trademarks of specific equipment, instruments or materials is due to identification purposes, there being no promotional commitment in relation to them, neither by the authors nor by the publisher.
References
Acevedo, D., Builes, S., Ordóñez, C. & López, I. 2011. Evaluación de la eficiencia de una batería de filtros empacados en zeolita en la remoción de metales pesados presentes en un licor mixto bajo condiciones de laboratorio. Revista Ingenierías Universidad de Medellín, 10(18), 31-42.
Can, Ö., Balköse, D., & Ülkü, S. 2010. Batch and column studies on heavy metal removal using a local zeolitic tuff. Desalination, 259(1-3), 17–21. doi:10.1016/j.desal.2010.04.047
Carreño, U.F. 2015. Tratamientos de aguas industriales con metales pesados a través de zeolitas y sistemas de biorremediación. Revisión del estado de la cuestión. Revista Ingeniería, Investigación y Desarrollo, 15(1), 70-78.
Ciosek A.L., Luk G.K. 2017. Kinetic Modelling of the Removal of Multiple Heavy Metallic Ions from Mine Waste by Natural Zeolite Sorption. Water, 9(7), 482. doi:10.3390/w9070482
Chiang, Y. W., Ghyselbrecht, K., Santos, R. M., Martens, J. A., Swennen, R., Cappuyns, V., & Meesschaert, B. 2012. Adsorption of multi-heavy metals onto water treatment residuals: Sorption capacities and applications. Chemical Engineering Journal, 200-202, 405–415. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2012.06.070
Choi, H.-J., Yu, S.-W., & Kim, K. H. 2016. Efficient use of Mg-modified zeolite in the treatment of aqueous solution contaminated with heavy metal toxic ions. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 63, 482–489. doi:10.1016/j.jtice.2016.03.005
Delkash, M., Ebrazi Bakhshayesh, B., & Kazemian, H. 2015. Using zeolitic adsorbents to cleanup special wastewater streams: A review. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 214, 224–241. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.04.
Du, G. 2012, Retention and transport throughFe (III)-coated natural zeolite. J. Hazard. Mater. Journal of Hazardous Materials. 221–222, 118–123.
Guocheng, L., Li, Z., Wei-Teh, J., Ackley, C. & Fenske, N. 2014. Demarco removal of Cr (VI) from water using Fe (II)-modified natural zeolite. Chem. Eng. Chemical Engineering Researchand Design, 92(2), 384–390. doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2013.08.003
Jovanovic, B., Vukasinovic-Pesic, V., Veljovic, D., & Rajakovic, L. 2011. Arsenic removal from water using low-cost adsorbents: A comparative study. Journal of the Serbian Chemical Society, 76(10), 1437–1452. doi:10.2298/jsc101029122j
Kim, D.-G., Nhung, T. T., & Ko, S.-O. 2016. Enhanced adsorption of heavy metals with biogenic manganese oxide immobilized on zeolite. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 20(6), 2189–2196. doi:10.1007/s12205-016-0356-1
Magriotis, Z., Paulo, V. & Leal, A. 2014. Treatmentthrough zeolites etheramines. Applied Clay Science 91–92, 55–62.
Malamis, S., & Katsou, E. 2013. A review on zinc and nickel adsorption on natural and modified zeolite, bentonite and vermiculite: Examination of process parameters, kinetics and isotherms. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 252-253, 428–461. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.03.024
Margeta, K., Zabukovec, N., Siljeg, M., & Farkas, A. 2013. Natural Zeolites in Water Treatment – How Effective is Their Use. Water Treatment. doi:10.5772/50738
Ríos, A., Vargas, F. & Cuchimaque, L. 2013. Remoción de Fe y Mn en aguas naturales por adsorción-oxidación sobre clinoptilolita. Rev. Fac. Ing. Univ. Antioquia, (66), 24-44.
Shi, J., Yang, Z., Dai, H., Lu, X., Peng, L., Tan, X., Fahim, R. 2018. Preparation and application of modified zeolites as adsorbents in wastewater treatment. Water Science and Technology, wst2018249. doi:10.2166/wst.2018.249
Wang, S., & Peng, Y. 2010. Natural zeolites as effective adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Chemical Engineering Journal, 156(1), 11–24. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2009.10.029
Wen, J., Dong, H., & Zeng, G. 2018. Application of zeolite in removing salinity/sodicity from wastewater: A review of mechanisms, challenges and opportunities. Journal of Cleaner Production, 197, 1435–1446. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.06.270.